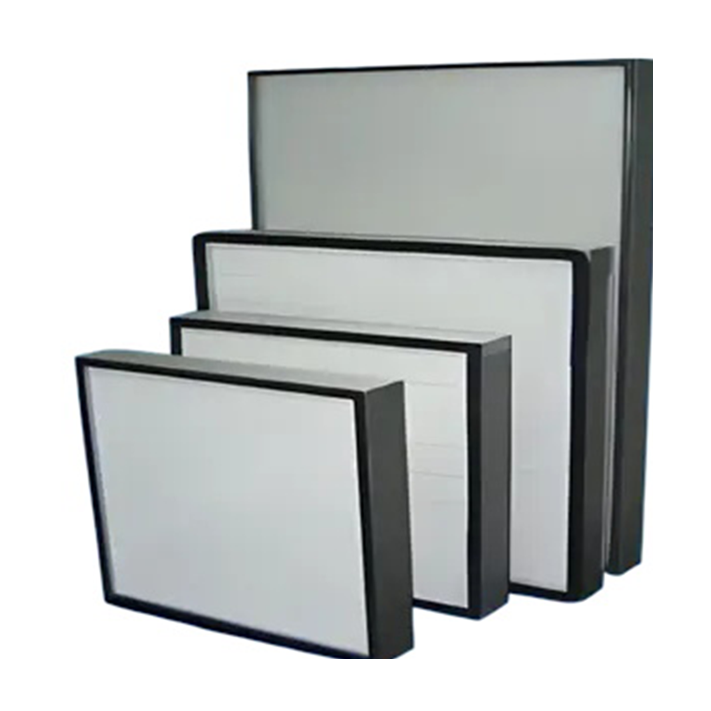
Brief Introduction
The high-efficiency filter is primarily used to capture dust particles smaller than 0.5um and various other suspended solids. It employs ultra-fine glass fiber paper as the filtering material, with offset paper, aluminum foil, and other materials serving as partitions, all framed with wood and aluminum alloy.

Detailed Introduction to High Efficiency Filters
High-efficiency filters are mainly used to capture dust particles smaller than 0.5um and various suspended solids. Ultra-fine glass fiber paper serves as the filtering material, while offset paper, aluminum foil, and other materials act as partitions, all framed with wood and aluminum alloy.
Each unit is tested using the nanoflame method and features high filtration efficiency, low resistance, and a large dust-holding capacity. They are widely used in air supply systems for air conditioners in dust-free workshops for optical electronics, LCD production, biomedicine, precision instruments, beverages and food, PCB printing, and other industries. High-efficiency and ultra-high-efficiency filters are typically installed at the end of cleanrooms. Based on their structural design, they can be categorized into: partitioned, non-partitioned, high-air-volume, ultra-high-efficiency filters, etc.
Additionally, there are three types: ultra-high-efficiency filters, which can achieve 99.9995% cleanliness; antibacterial non-partitioned filters, which prevent bacterial infiltration into cleanrooms; and low-efficiency filters, which are cost-effective and suitable for low-filtration requirements.
General Principles for Filter Selection
1. Inlet and Outlet Diameter:
The inlet and outlet diameters should not be smaller than the pump's inlet diameter and should generally match the pipeline diameter.
2. Rated Pressure:
Determine the filter's pressure rating based on the maximum possible pressure in the pipeline.
3. Pore Size Selection:
Primarily consider the size of particles to be filtered, determined by process requirements. Refer to the "Filter Technical Specifications" table for details.
4. Filter Material:
The filter material should match the pipeline material. For different service conditions, consider cast iron, carbon steel, low-alloy steel, or stainless steel.
5. Pressure Loss Calculation
For water filters, the pressure loss is typically 0.52~1.2 kPa at the rated flow rate.
Technical Features
1. Simple and compact design, easy installation and removal;
2. Short backwash time, low pressure loss, and minimal water consumption;
3. High filtration accuracy, suitable for various water types;
4. Smart control system for remote operation;
5. Equipped with motor overload protection for safety and reliability;
6. Continuous water supply during cleaning and drainage;
7. Long lifespan with no need for replacement.
Installation Requirements
1. Technical specifications must match the pipeline. If the filter's capacity is insufficient, install multiple filters in parallel;
2. Install near the pressure source for optimal protection;
3. Install in series with a check valve at the outlet to prevent backflow;
4. Ensure water temperature does not exceed the filter's rated limit;
5. Installation site must have 380V three-phase power and a drainage pipe no longer than 5 meters;
6. Monitor filtration accuracy and use timers carefully;
7. Ensure the environment is waterproof, rainproof, and moisture-proof.
1. Water enters the filter core from the inlet;
2. Flows outward through the filter mesh;
3. Contaminants accumulate on the inner surface, forming a filter cake;
4. When pressure differential exceeds a set value, the filter initiates automatic cleaning.
Features
1. High filtration accuracy: removes over 95% of suspended solids and reduces organic matter, viruses, bacteria, colloids, iron, and other impurities. Output turbidity is below 1NTU when input is 10NTU;
2. Fast filtration speed: typically 40m/h, up to 60m/h, three times faster than conventional sand filters;
3. High dirt-holding capacity: 15-35kg/m³, four times higher than conventional filters;
4. Low backwash water consumption: less than 1-2% of filtered water volume per cycle;
5. Low chemical usage and operating costs: coagulant dosage is half to one-third of conventional methods;
6. Compact footprint: one-third the size of conventional sand filters;
7. Adjustable parameters: filtration accuracy, retention capacity, and anti-clogging can be customized;
8. Durable filter material with a lifespan exceeding 20 years.
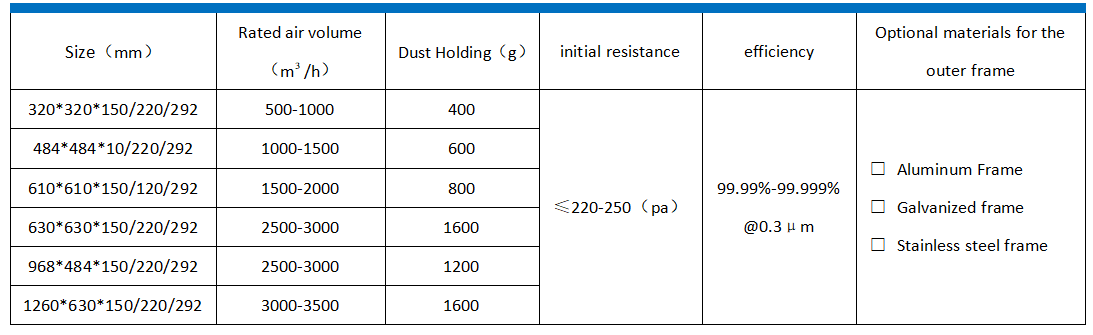
Technical parameters of high-efficiency filter without partition:
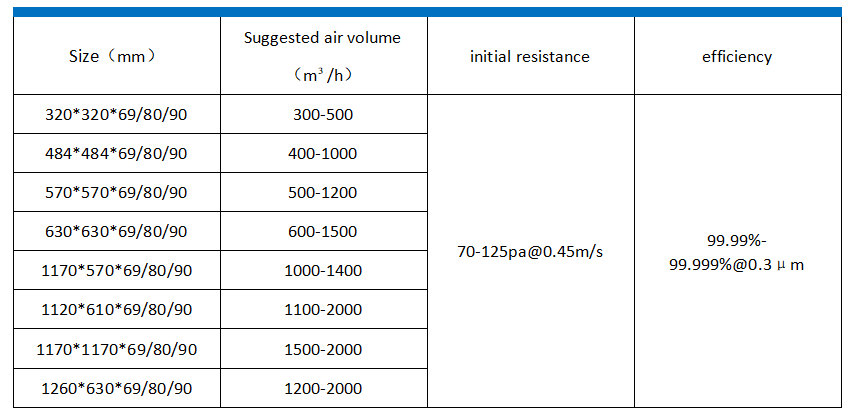
Technical parameters of high-efficiency filters with partitions: